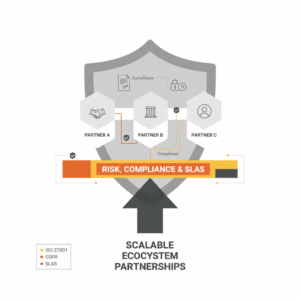
Why risk, compliance, and SLAs must lead ecosystem strategy
Partnership leaders shape outcomes when they treat risk, compliance, and service level agreements as the spine of the ecosystem, not an afterthought. Executive teams often move fast to unlock capability, coverage, or cost advantages through partners. The same teams stumble when exposure, accountability, and service expectations are ambiguous. A clear control framework, a living compliance posture, and measurable SLAs convert partner intent into reliable performance. This article defines the operating mechanics that C-suite, CX leaders, and service owners can deploy to make partnerships safe, auditable, and scalable.¹²
What is “risk and compliance” in ecosystem partnerships?
Partnership risk is the potential for loss or harm arising from a third party’s technology, process, people, or data handling. Compliance is the ability to show, with evidence, that controls meet laws, regulations, contracts, and standards. In modern service ecosystems, common control languages anchor alignment. ISO/IEC 27001 defines how to run an information security management system across the enterprise and its suppliers.¹ NIST SP 800-53 catalogs security and privacy controls for systems and organizations, including supply chain risk controls.² GDPR and the Australian Privacy Act define obligations for personal data, including transparency, lawful basis, and rights management.³⁴⁸ APRA CPS 234 requires regulated entities to manage information security and notify significant incidents, including those arising at service providers.⁵ These references set shared expectations and reduce interpretive drift across partners.¹²³⁴⁵⁸
How do you operationalize control frameworks across a partner chain?
Leaders make frameworks real by translating them into testable partner obligations. Define a minimum control baseline using NIST SP 800-53 families to cover access, incident response, business continuity, and supplier risk.² Require an auditable security management system aligned to ISO/IEC 27001 to ensure controls are not point fixes but part of a continuous plan-do-check-act cycle.¹ Map data protections to GDPR Articles and Australian Privacy Principles so privacy controls reflect legal duties, not just policy language.³⁸ For cardholder data, require PCI DSS v4.0.1 controls where payment flows exist and request the Council’s summary of changes to validate a partner’s transition plan.¹¹ The combination turns abstract assurance into practical evidence you can assess quarterly.¹²³⁴⁵¹¹
Where do SOC 2, ITIL, PCI, and COBIT fit together?
Executives orchestrate complementary standards instead of debating which single badge is “best.” SOC 2 reports provide independent assurance over controls relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, or privacy. They help you verify that a service organization’s control design and operation have been examined by an independent CPA.⁶ COBIT offers a governance frame to link strategy, risk, and performance, and to right-size control objectives by design factors.¹² ITIL 4’s Service Level Management practice helps define business-based targets for utility, warranty, and experience, which become the contract terms you monitor.¹³¹⁸ PCI DSS v4.0.1 sets payment security baselines when card data is present.¹¹ Each standard serves a different lens. Together they provide governance, control verification, service management, and domain-specific safeguards.⁶¹¹¹²¹³¹⁸
What makes a “good” SLA in a partner model?
Strong SLAs make reliability observable. Define service level indicators that reflect the customer journey, not just the supplier’s subsystem. Measure availability, latency, correctness, and durability where they matter. Use service level objectives that balance ambition and cost, then enforce an error budget policy to govern change when targets are missed. Error budgets create a predictable response to degradation and keep reliability and feature delivery in balance.¹⁴¹⁵ Document objectives, measurement windows, exclusions, and escalation paths so both parties can audit behavior during incidents. ITIL 4 provides practice guidance on setting clear business-based targets and managing assessment against them.¹³¹⁸
How should leaders tier SLAs across a multi-partner journey?
CX leaders increase resilience when they tier SLAs by criticality. Start with customer-visible transactions, then cascade to upstream and downstream dependencies. Use a top-level objective such as end-to-end checkout success or first-contact resolution, then allocate budgets to each partner based on contribution to risk. Calibrate windows and thresholds to reflect when customers feel pain. Pair this with shared runbooks and time-boxed joint incident response commitments to reduce mean time to restore. The Google SRE approach shows how to write SLOs and apply error budgets to freeze change when risk spikes.¹⁴¹⁵ In parallel, use COBIT governance objectives to align risk appetite and escalation authority with the service’s value.¹²
Which compliance artifacts should you collect and how often?
Executives should request artifacts on a quarterly or semiannual cadence, aligned to risk. Seek current SOC 2 reports with a mapping to your control requirements, including subservice organizations.⁶ Request ISO/IEC 27001 certificates and statements of applicability to see which controls are in scope.¹ Ask for NIST SP 800-53 control mappings where governmental or regulated workloads exist.² For privacy, collect GDPR Article 30 records of processing, DPIAs for high-risk activities, and evidence of Australian Privacy Principles training and complaint handling.³⁸ For payment flows, obtain PCI DSS v4.0.1 Attestations of Compliance or Self-Assessment Questionnaires and review the Summary of Changes to understand any gaps in transition.¹¹¹⁶ APRA-regulated partners must evidence CPS 234 incident notification capabilities and board-level accountability.⁵ These artifacts convert trust into verified assurance.
How do you manage shared incidents across multiple providers?
Partnerships stress during incidents. Leaders pre-commit to a joint incident command structure with clear roles, evidence capture, and regulatory triggers. Use a common taxonomy for severity, customer impact, and data categories. Align on notification timeframes required by GDPR, OAIC, and APRA CPS 234 where applicable, then bake those into your SLAs.³⁵⁸ Require partners to maintain 24×7 incident contacts, to participate in post-incident reviews, and to share corrective actions that trace to control owners and deadlines. NIST SP 800-53 provides control families for incident response and contingency planning that you can adopt as acceptance criteria for partner onboarding and renewal.²
What risks matter most in modern CX ecosystems?
Service leaders face four systemic risks. First, data protection risk grows with data sharing; GDPR, APPs, and sector rules raise the cost of missteps.³⁸ Second, availability risk compounds with dependency chains; end-to-end SLOs and error budgets reduce fragility.¹⁴ Third, change risk emerges from frequent releases; a freeze policy tied to error budget burn keeps delivery safe.¹⁵ Fourth, compliance drift accumulates as partners scale; COBIT governance and ISO 27001’s continuous improvement loop counter that drift with cadence and accountability.¹¹²¹
How do you measure and report ecosystem health to the board?
Boards want evidence, not anecdotes. Build a partner risk register that maps each service to data classes, control obligations, and SLA tiers. Report three executive KPIs. First, SLA reliability versus SLO targets and error budget consumption, split by business capability.¹⁴¹⁵ Second, control assurance coverage across ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS artifacts versus plan.¹⁶ Third, regulatory readiness measured by time to detect, time to notify, and time to contain for notifiable incidents under GDPR, OAIC, and APRA CPS 234.³⁴⁵ Present these KPIs alongside remediation velocity to show momentum. Use COBIT to ensure measures align to enterprise goals and value delivery.¹²
What is the practical playbook for partnership onboarding?
Leaders accelerate safe onboarding when they follow a sequenced playbook. Define the business capability, customer promise, and data footprint first. Select control baselines from NIST SP 800-53, then map legal obligations including GDPR and APPs.²³⁸ Require evidence packages: SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS where relevant, and CPS 234 alignment for regulated partners.⁵⁶¹¹ Negotiate SLAs that translate SLOs into contract terms with measurement, exclusions, and error budget response.¹³¹⁴ Stand up joint incident response, notification pathways, and a post-incident review template. Finally, schedule quarterly service reviews that refresh risks, test controls, and tune SLAs to current demand. Treat the playbook as a reusable asset across the ecosystem.
What is the business impact when risk and SLAs are first-class?
Customer trust grows when services meet promises predictably and when issues are handled with speed, clarity, and accountability. Operating costs fall when partners share a common control language and when evidence flows cleanly into audits. Time to market accelerates when error budgets provide a rational, data-driven way to balance reliability and change.¹⁴ Boards gain confidence when reporting reflects recognized standards such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, COBIT, and PCI DSS.¹⁶ The organization gains negotiating power because assurance is measurable, repeatable, and comparable across vendors. The ecosystem gets safer, and customers notice.
What should you do next to raise partnership reliability?
Executives can act this quarter. Select a critical customer journey and define two or three end-to-end SLOs with clear SLIs.¹⁴ Map current partners to control baselines from NIST SP 800-53 and confirm ISO 27001 or SOC 2 coverage with current certificates and reports.¹²⁶ Validate privacy compliance against GDPR Articles and Australian Privacy Principles for that journey.³⁸ Confirm PCI DSS scope for any payment touchpoints and review v4.0.1 transition plans.¹¹ Establish a joint incident command charter across all involved providers with regulatory triggers for OAIC and APRA CPS 234 if applicable.⁴⁵ Convert these steps into contract addenda at renewal, then scale to adjacent journeys.
FAQ
What is the minimum compliance baseline for a new CX partner handling personal data?
A practical baseline requires an ISO/IEC 27001-aligned security management system, controls mapped to NIST SP 800-53, and privacy controls aligned to GDPR and the Australian Privacy Principles. Collect a current SOC 2 report when the provider processes customer data at scale.¹²³⁴⁶⁸
How should CX leaders write SLAs that support customer outcomes?
Leaders define SLIs and SLOs that reflect customer experience, such as availability and latency for critical transactions, then govern change with an error budget policy. Align wording with ITIL 4 Service Level Management so targets are business-based and auditable.¹³¹⁴¹⁸
Which standard confirms payment security in partner networks?
Use PCI DSS v4.0.1 for any flow involving cardholder data. Ask for Attestations of Compliance or applicable Self-Assessment Questionnaires and review the Council’s Summary of Changes to validate transition plans.¹¹¹⁶
Who should own regulatory notifications during a joint incident?
The contracting entity should own notifications, but partners must support evidence capture and timelines required by GDPR, the OAIC under the Privacy Act, and APRA CPS 234 where applicable. Bake roles and timeframes into SLAs and runbooks.³⁴⁵⁸
What governance framework links partner controls to enterprise value?
COBIT 2019 provides enterprise governance of information and technology with design factors to tailor control objectives. Use COBIT to align risk appetite, metrics, and escalation to business goals.¹²
Which assurance report do executives request from SaaS partners?
Executives typically request a SOC 2 report that covers the Trust Services Criteria relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, or privacy. Validate the reporting period, scope, subservice organizations, and exceptions.⁶
Which artifacts prove SLA reliability over time?
Maintain signed SLO documents, monthly SLI reports, error budget burn charts, and post-incident reviews that trace to corrective actions. Google SRE material provides templates for SLOs and error budget policies that you can adapt.¹⁴¹⁵
Sources
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 — International Organization for Standardization — 2022 — Standard overview. https://www.iso.org/standard/27001
NIST Special Publication 800-53 Rev. 5 — Ross et al. — 2020 — National Institute of Standards and Technology. https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-53r5.pdf
Regulation (EU) 2016/679 General Data Protection Regulation — European Union — 2016 — EUR-Lex. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj/eng
The Privacy Act 1988 — Office of the Australian Information Commissioner — 1988, current guidance page — OAIC. https://www.oaic.gov.au/privacy/privacy-legislation/the-privacy-act
CPS 234 Information Security — Australian Prudential Regulation Authority — 2019 — APRA Handbook. https://handbook.apra.gov.au/standard/cps-234
SOC 2 — Trust Services Criteria — AICPA & CIMA — 2023 resource hub — AICPA. https://www.aicpa-cima.com/topic/audit-assurance/audit-and-assurance-greater-than-soc-2
COBIT 2019 Fact Sheet — ISACA — 2020 — ISACA. https://www.isaca.org/about-us/-/media/4fc9d51512c54465b95c418d1468baef.ashx
Australian Privacy Principles — OAIC — 2014, current guidance page — OAIC. https://www.oaic.gov.au/privacy/australian-privacy-principles
PCI DSS Document Library and PCI DSS v4.0.1 — PCI Security Standards Council — 2024 — PCI SSC. https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/document_library/
ITIL 4 Practitioner: Service Level Management — PeopleCert — 2023 — PeopleCert. https://www.peoplecert.org/browse-certifications/it-governance-and-service-management/ITIL-1/itil-4-practitioner-service-level-management-3867
Error Budget Policy — Google SRE Workbook — Beyer et al. — 2016 — Google. https://sre.google/workbook/error-budget-policy/
Example SLO Document — Google SRE Workbook — Beyer et al. — 2016 — Google. https://sre.google/workbook/slo-document/
PCI DSS v4.0.1 announcement — PCI SSC — 2024 — PCI SSC Blog. https://blog.pcisecuritystandards.org/just-published-pci-dss-v4-0-1
COBIT resource hub — ISACA — 2019, updated — ISACA. https://www.isaca.org/resources/cobit
Concepts in service monitoring and SLOs — Google Cloud Observability — 2025 — Google Cloud. https://cloud.google.com/stackdriver/docs/solutions/slo-monitoring