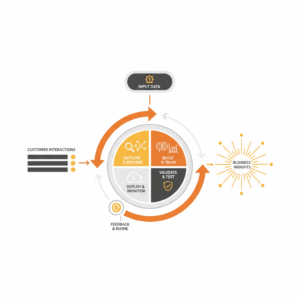
Why do CX leaders need a model lifecycle audit now?
Executives face rising expectations, tighter privacy rules, and models that change when data or context shifts. A model lifecycle audit gives leaders a single, repeatable workflow to verify that data is lawful, models are reliable, and outcomes are fair. It turns ad hoc checks into a living assurance system. Modern guidance supports this approach and recommends risk-based controls across the full AI system lifecycle, from business framing to retirement.¹ The audit described here focuses on customer experience, contact centres, and service operations, where model-driven decisions shape eligibility, routing, retention, and agent assist.
What is a model lifecycle audit?
A model lifecycle audit is a structured assessment of the artefacts, controls, and evidence that prove a model is fit for purpose. It covers data lineage, consent, feature engineering, training, evaluation, deployment, monitoring, incident response, and retirement. The audit uses canonical documentation patterns to make evidence portable and readable by humans and machines. Model Cards capture purpose, performance, and limitations at release.² Datasheets for Datasets document provenance, collection context, and intended use.³ Together these artefacts form the authoritative record that links business intent to measurable outcomes.
How do you frame scope and risk before you start?
Leaders start with a risk screen. Define the decision, the customer impact, and the harm if the model fails. Use a taxonomy that distinguishes assistive tooling from automated decisions and classifies data sensitivity, including identity attributes and special categories. A risk-based inventory aligns to emerging AI management standards that ask organizations to catalogue systems, risks, and controls with accountable owners.⁴ This early scoping step sets audit depth. High-risk decisions require stronger evidence, tighter monitoring, and rigorous rollback plans. Lower-risk use cases still need traceability and testing but with lighter-weight documentation.
Which data controls prove that identity and consent are solid?
Auditors verify that identity data is accurate, linked, and governed. They check that customer identifiers follow master data policies and that consent signals are captured, versioned, and enforced. The audit applies the FAIR data principles to ensure data is findable, accessible with controls, interoperable, and reusable with clear metadata.⁵ Teams include a dataset register, lineage diagrams from raw to feature tables, and retention rules that match policy. A strong data foundation reduces feature drift and supports reproducibility. Mature data management frameworks recommend stewardship roles, quality rules, and escalation paths so data issues do not become model incidents.⁶
How do you test features, training code, and evaluation rigor?
Teams validate feature definitions and unit test transformations. They snapshot training data, pin library versions, and record hyperparameters. Hidden complexity often lives outside the model in pipelines and glue code, so engineers treat infrastructure and orchestration as first-class audit targets.⁷ Evaluation moves beyond a single metric. Auditors expect stratified performance by segment, channel, and geography, with calibration checks and stability under realistic perturbations. An ML Test Score approach encourages a balanced suite of tests across data, model, and deployment, instead of relying on accuracy alone.⁸ This discipline prevents brittle models that perform well only in ideal conditions.
How do you document decisions for CX, legal, and engineering audiences?
Clear documentation reduces rework and speeds approvals. Model Cards express purpose, context, metrics, and ethical considerations in a concise, standard format.² Datasheets describe data collection methods, licensing, and known biases.³ Release notes link code commits to training runs and evaluation reports. Traceability maps business requirements to model objectives and KPIs. When documentation follows open patterns, regulators, internal audit, and partners can understand claims quickly. Standards bodies now emphasize explicit roles, processes, and continual improvement in AI management systems, which aligns with maintaining these artefacts as living documents.⁴
How do you operationalize monitoring and incident response?
Good teams treat monitoring as a product. They track input data quality, feature drift, output distributions, and business KPIs. They set thresholds with clear runbooks that define who gets paged, what gets rolled back, and how to communicate customer impact. Post-incident reviews feed back into tests and documentation. This operational focus counters technical debt that accrues as models interact with real systems.⁷ Monitoring also includes policy signals such as consent withdrawal and preference changes, which must disable or reroute specific processing paths in near real time. Privacy regulators highlight the need for accountable practices and timely responses to customer requests.⁹
How do you assess fairness and explainability in customer decisions?
CX leaders measure fairness by comparing error rates and positive outcomes across meaningful cohorts. They prefer diagnostic slices that align with service reality, such as first-contact resolution by segment or wait-time predictions by language group. Model Cards can include fairness assessments and known limitations, with guidance on safe operating ranges.² Explainability focuses on decision transparency rather than recipe disclosure. The goal is to help agents and customers understand factors that drove a decision, within privacy and security limits. Risk frameworks recommend testing and documenting impacts on affected individuals, especially where automated decisions influence rights or access.¹
How do you govern deployment, change, and retirement?
Every production model needs a clear owner, versioning, and a change calendar. Release gates confirm that documentation, tests, and security checks are complete. Canary deployments reduce impact by exposing a fraction of traffic first. When business context changes, teams conduct targeted re-validation and deprecate models with a retirement plan that archives artefacts for audit. A management system standard for AI formalizes these governance loops so organizations can demonstrate control to boards and regulators.⁴ In practice, the same discipline that ships models also retires them cleanly to avoid phantom dependencies and unintended processing.
How do you measure value and keep the audit living?
Leaders measure impact in business and customer terms. They link model outputs to conversion, handling time, containment, satisfaction, and complaints. They separate model lift from channel or campaign effects with holdout designs. Monitoring closes the loop by alerting when lift degrades or fairness metrics drift. Teams schedule periodic audit refreshes to reconfirm consent, data quality, and evaluation robustness. A repeatable cadence enables continuous compliance with territorial privacy rules and upcoming AI legislation. The EU has adopted a regulation on AI that introduces obligations based on risk class and lifecycle controls, which reinforces the need for durable audit evidence.¹⁰
What is the step-by-step workflow you can run this quarter?
Leaders can run an eight-step workflow that scales from pilot to portfolio.
Create an AI system inventory with risk classification and accountable owners.⁴
Register datasets with Datasheets and lineage diagrams, and align them to FAIR and policy controls.³ ⁵
Define testable objectives and segment-level evaluation plans, then snapshot training data and code.⁸
Produce a Model Card at release with performance, calibration, and limitations.²
Establish monitoring for data, drift, outcomes, and consent signals with on-call runbooks.⁷
Set change management gates with canary deploys and rollback plans.⁴
Run periodic fairness and explainability reviews with customer-relevant slices.¹
Retire or retrain with archived artefacts and post-incident learning, and recertify models on context changes.⁷
This workflow embeds assurance into daily work. It scales across contact centre routing, next-best-action, and agent assist, without slowing delivery.
What should executives do next to unlock value safely?
Executives should appoint a single owner for the model lifecycle audit, fund a central registry, and require Model Cards and Datasheets for every release. They should align governance to a recognized AI management standard, integrate privacy signals into monitoring, and set quarterly audit refreshes. They should insist on business-level impact metrics, not just model metrics. The organizations that lead in customer experience combine disciplined audit evidence with fast iteration. They build trust with customers and regulators by proving that models are effective, fair, and reversible when needed. With this workflow, leaders can scale AI in service and contact centres with confidence and speed.¹
FAQ
How does a model lifecycle audit reduce CX risk in contact centres?
A model lifecycle audit creates a risk-based inventory, documents data provenance and consent, standardizes release artefacts with Model Cards and Datasheets, and sets up monitoring with defined runbooks. Together these controls reduce failure modes in routing, eligibility, and agent assist by making decisions traceable and reversible.¹ ² ³ ⁸
What documentation should we require for every model release?
Require a Model Card that states purpose, metrics, limitations, and fairness slices, and a Datasheet for Datasets that covers provenance, collection context, and licensing. Link these to code commits, training snapshots, and evaluation reports so auditors can trace results to inputs.² ³
Which standards or frameworks align with this audit workflow?
The workflow aligns with the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, ISO/IEC 42001 AI management systems, and organizational data governance practices such as DAMA DMBOK. These sources emphasize lifecycle controls, accountable ownership, and continuous improvement.¹ ⁴ ⁶
Why do FAIR data principles matter for identity and consent?
FAIR principles ensure data is findable with metadata, accessible under controls, interoperable across systems, and reusable with provenance. Applying FAIR to identity and consent data improves traceability and reduces feature drift that can degrade model performance.⁵
Who should own the model lifecycle audit in an enterprise?
Assign ownership to a cross-functional leader accountable for risk, privacy, and delivery. This role maintains the system inventory, enforces documentation standards, and chairs incident reviews so that engineering, CX, legal, and compliance remain aligned.⁴ ⁹
Which tests move the needle beyond accuracy?
Adopt an ML Test Score approach that covers data validation, feature tests, calibration, robustness checks, and stratified performance by customer segment and channel. This balanced test suite prevents brittle releases and supports safer canary rollouts.⁸
What triggers a re-audit or model retirement?
Trigger a re-audit when data sources change, consent policies update, performance drifts beyond thresholds, or regulations shift. Retire models that no longer meet evaluation standards or business objectives, and archive artefacts for traceable decommissioning.⁴ ⁷
Sources
NIST AI Risk Management Framework 1.0. NIST. 2023. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
Model Cards for Model Reporting. Mitchell et al. FAT* 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.03993
Datasheets for Datasets. Gebru et al. Communications of the ACM, 2021. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09010
ISO/IEC 42001:2023 Artificial Intelligence Management System. ISO. 2023. https://www.iso.org/standard/81230.html
The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Wilkinson et al. Scientific Data, 2016. https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata201618
DAMA-DMBOK2: Data Management Body of Knowledge. DAMA International. 2017. https://www.dama.org/publications/dama-dmbok
Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems. Sculley et al. NeurIPS, 2015. https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2015/hash/86df7dcfd896fcaf2674f757a2463eba-Abstract.html
The ML Test Score: A Rubric for ML Production Readiness. Breck et al. 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.09223
Australian Privacy Principles guidelines. OAIC. 2020. https://www.oaic.gov.au/privacy/australian-privacy-principles
EU Artificial Intelligence Act adopted. European Parliament. 2024. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/press-room/20240308IPR19015/eu-artificial-intelligence-act-parliament-approves-the-first-rules-for-ai